By Rida Fatima and Muhammad Zubair Ali
Air pollution poses a severe threat to human health, ecosystems, and the global economy, driven by industrial, transportation, agricultural, and domestic activities that emit harmful pollutants, leading to serious health issues, environmental degradation, and significant economic costs.
Addressing this pressing issue requires a multifaceted approach. Embracing renewable energy sources, enhancing fuel and energy efficiency, supporting sustainable agricultural practices, and enforcing stricter emissions regulations are critical steps. Equally important are public awareness campaigns and international efforts, such as the Paris Agreement, which underscore the need for immediate and collective action. Governments, industries, and individuals must collaborate to safeguard our future.
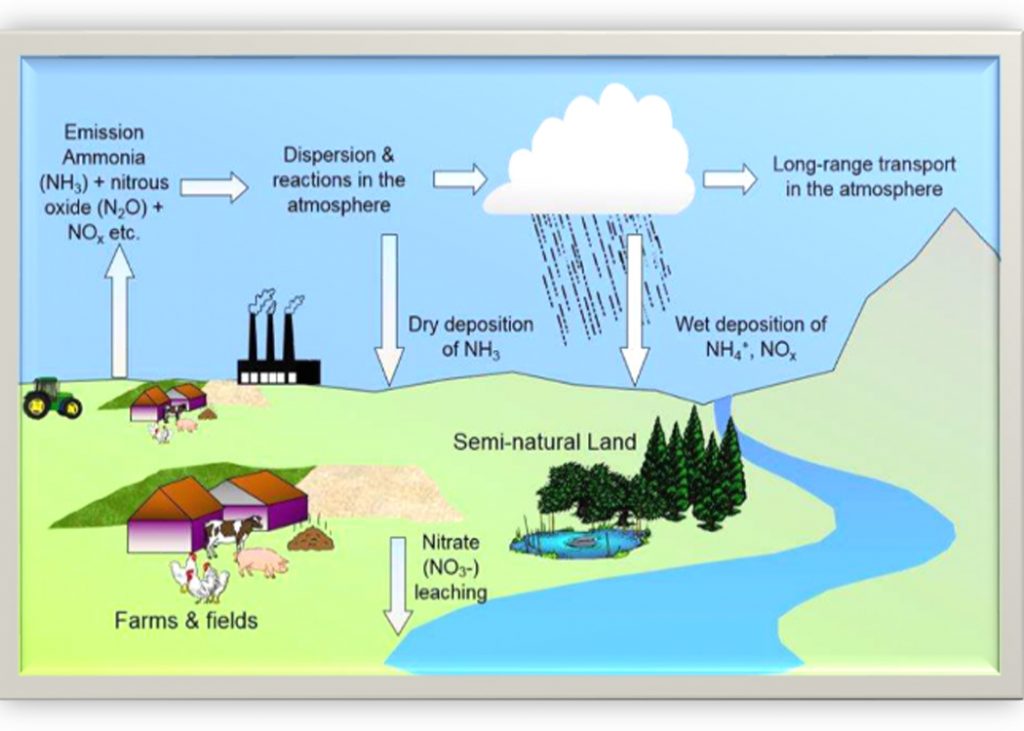
Industries are major contributors to air pollution, primarily through the combustion of fossil fuels for energy and various industrial processes. Power plants, manufacturing facilities, and construction sites are among the largest sources, releasing pollutants like particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. These emissions not only pose severe health risks but also lead to environmental issues such as acid rain and ozone layer depletion. To mitigate these impacts, the adoption of cleaner energy sources, improved energy efficiency, and the enforcement of stricter regulations are essential.
Transportation remains a significant source of air pollution, with emissions from vehicles, including cars, trucks, and airplanes, contributing heavily to the problem. These sources release nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds, all of which exacerbate respiratory issues and contribute to climate change through the emission of greenhouse gases. Solutions lie in transitioning to electric or hybrid vehicles, adopting cleaner fuels, and promoting alternative modes of transportation, such as public transit, walking, and cycling.
Agricultural practices, particularly the burning of waste and the use of fertilizers and pesticides, release harmful pollutants like particulate matter and nitrogen oxides. These activities contribute to health problems and environmental issues, including ground-level ozone formation and deforestation. Sustainable farming practices and effective waste management are key strategies for reducing agricultural pollution.
Everyday household activities, including cooking and heating with fossil fuels, using chemical cleaning products, and improper waste disposal, also contribute to air pollution. The pollutants generated, such as particulate matter and volatile organic compounds, pose significant health risks. Mitigation strategies include switching to cleaner energy sources, using eco-friendly products, and adhering to proper waste disposal practices.
Greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels are a leading cause of global warming. Pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and particulate matter, which trap heat and accelerate climate change. These pollutants also disrupt heat distribution and precipitation patterns, underscoring the need for comprehensive efforts to reduce air pollution.
Air pollution disrupts ecosystems, harming plant growth and animal populations. Pollutants like ozone and particulate matter can reduce plant diversity and negatively affect animal habitats, behavior, and health. This leads to ecosystem degradation and a loss of biodiversity, which in turn impacts essential services such as pollination and pest control.
Pollutants can acidify soil and introduce heavy metals, negatively affecting plant growth and posing risks to human health. Acid rain, for example, reduces soil fertility, while contaminants can enter the food chain, disrupting ecosystems and altering nutrient cycles.
Addressing air pollution demands a shift toward cleaner energy sources, enhanced energy efficiency, and adopting pollution-reducing technologies. Strengthening regulations, raising public awareness, and investing in green infrastructure are also crucial. These measures can significantly improve air quality, protecting human health and the environment.






