By Dr Maria Jamil, Department of Pathology, Faculty of veterinary science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Dr Aisha Khatoon, Department of Pathology, Faculty of veterinary science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Dr Muhammad Kashif Saleemi, Department of Pathology, Faculty of veterinary science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Dr Muhammad Tahir Aleem, MOE Joint International Research Laboratory of Animal Health and Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, 210095 Nanjing, P.R.China
“DNA Vaccination is a transferring of specific antigen DNA coding sequence onto the cells of an immunized species.”
For the sufficient growth of the poultry sector, proper health management of birds is essential. Several diseases affect the birds and lead to a probable threat to the poultry sector through large economic losses. Against infectious diseases are extensively followed a vaccine, while conventional vaccines have definitive drawbacks. Advances in recombinant DNA technology leads to the development of new generation vaccines as a safe replacement to the traditional vaccines. Compared to genetic protein DNA vaccine has one or more genes encoding that offers several benefits over the conventional vaccines. In DNA vaccine, antigens’ appearance in the target host resembles native pathogen epitopes and hence preserve the protein structure and antigenicity than the traditional vaccines.
Furthermore, DNA vaccine is capable to effectively produce both cellular and humoral immune response to protein antigen and therefore efficient against a large number of pathogens. Simultaneously, the effectiveness of the DNA vaccine in birds depends on several factors apart from their efficiency. They are comparatively cost-effective, easily administer and stable under field conditions. Furthermore, as poultry is a food animal, the presence of vaccine residues in tissues is detrimental. This has been prevented through the intradermal (ID) and subcutaneous (SC) route of vaccine administration rather than the intramuscular route (IM).
The plasmid vector is easily constructed and may be stimulated rapidly and inexpensively compared to conventional vaccine. Additionally, a very minute amount (micrograms) plasmid vector may distribute numerous antigens in a single shot that offers immunity against various pathogens at once. All these factors markedly decline the expenses acquired through vaccination. The efficacy of the DNA vaccine may be improved through molecular adjuvants, i.e. toll-like receptor (TLR) ligand and cytokine. A prominent example of TLR ligand includes CpG (TLR21) and flagellin (TLR5) and cytokines, i.e., IFN-ɣ and IL-12. Various studies had documented that when DNA vaccines were administered along with TLR ligands and cytokines, this leads to Upregulation of immune response.
Advantage of DNA vaccines:
As compared to the conventional vaccine, stimulation of DNA vaccine is simple, economical and rapid.
- The DNA vaccine is more thermostable than the traditional vaccine, thus not required the cold chain.
- It eradicates the threat of reversion of pathogenic phenotypes
- In DNA vaccine exist antigen to both MHC-I and MHC-II molecules
- Only against an antigen of interest, the immune response provokes through DNA vaccine
- Cost-effective and easy to develop
- Natural infection mimics through DNA vaccine. Antigen protein looks like the standard eukaryotic structure and post-translational alteration.
Major poultry diseases and DNA vaccine antigens:
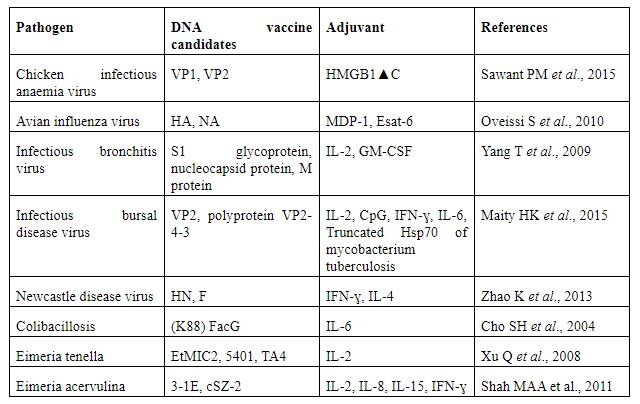
The poultry industry suffers various infectious diseases such as infectious bursal disease (IBD), infectious bronchitis (IB), Newcastle disease (ND), avian influenza virus (AI), and Eimeria species. Inactivated, as well as the live vaccine, is extensively used against such diseases in the poultry industry. At the same time, these vaccines are linked with their inherent drawbacks. Through several studies have been revealed that the DNA vaccine is effective against infectious diseases in poultry. Furthermore, without live pathogen DNA vaccine encodes antigenic proteins; it supports to prevent the existence of problem linked with reverted virulence, conflicting mutants and decrease the environmental pollution.
In chicken DNA vaccine, antigenic Protein encoding pathogen genes are used (specified in Table) and used molecular adjuvants to increase the efficiency of the vaccines’ efficiency.